Registration
Made Easy


YOUR LOCAL TAX AGENT
With over 25 years of dedicated accounting experience AMA Accountants brings a wealth of knowledge and proven expertise to the table. We’ve navigated economic shifts, adapted to evolving regulations, and consistently delivered accurate and insightful financial solutions for a diverse range of clients.
This extensive history allows us to anticipate challenges, offer proactive advice, and build long-lasting relationships based on trust and a deep understanding of your unique business needs.
You can rely on our seasoned team to provide reliable accounting services, strategic financial guidance, and the peace of mind that comes with knowing your financial matters are in experienced hands.
Tax Time 2025
AMA Accountants
Your Local Tax Agent
At AMA Accountants, one of the top accounting firms in Australia, we aim to offer exceptional financial services that can add value to your personal or business growth. With a team of professionals, we are dedicated to understanding your needs and maximising your success accordingly.

We specialize in providing comprehensive SMSF (Self-Managed Super Fund) services designed to empower you to take control of your retirement savings. Our team of experienced professionals offers expert guidance on all aspects of SMSF management, from establishment and compliance to investment strategies and reporting.

Our Xero training program is a comprehensive and immersive learning experience designed to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge needed to effectively utilize this powerful accounting software. Xero has revolutionized the way businesses manage their finances, and our training sessions delve deep into its extensive features and functionalities.

Outsourcing essential business services like bookkeeping, payroll, tax preparation, and accounting can be a highly strategic and advantageous move for many companies. By entrusting these critical financial and administrative functions to specialized outsource providers, businesses can tap into a wealth of expertise, efficiency, and cost savings.

Our AMA Accountants internship program provides a unique opportunity for aspiring professionals to gain hands-on experience in the dynamic field of finance and accounting. As a participant in our internship, you will have the chance to work alongside seasoned accountants learning the ins and outs of the industry firsthand.

Navigating the complexities of tax registration can be a daunting task for many businesses, but that's where our expert team steps in to provide invaluable assistance. We specialize in guiding entrepreneurs and companies through the process of Goods and Services Tax (GST) registration, ensuring they fulfill all the necessary requirements.

Our business name registration application is very simple and the process for registration of business is made online. AMA Accountants will lodge your ABN, TFN & GST application with your company information and some additional information and notify you when your ABN is registered and is ready to use.

AMA Accountant are BAS & GST professionals that are well-versed in the latest regulations and requirements, ensuring that your BAS and GST obligations are met with precision and efficiency. AMA Accountants take a hands-on, personalized approach to guiding our clients through every step of the process.
AMA Accountants
Why choose us?
Our Personal Touch
We understand that your financial situation is unique, not just a set of transactions. That's why we prioritise building a strong relationship with you, taking the time to truly understand your goals, challenges, and aspirations.
We are trusted
As a trusted accounting business, we pride ourselves on providing accurate, reliable, and insightful financial guidance to our clients. We understand that managing finances can be complex which is why we're dedicated to offering personalised solutions tailored to meet each client's unique needs.
25 years of experience
With over 25 years of dedicated accounting experience, AMA Accountants brings a wealth of knowledge and proven expertise to the table. We've navigated economic shifts, adapted to evolving regulations, and consistently delivered accurate and insightful financial solutions for a diverse range of clients.
AMA Accountants
We’re a Trusted and Professional Accounting Business
If you are looking for Certified & Qualified Accountants in Australia, you have arrived at the right place.
We are Xero Certified Gold Partners Accountants & Payroll Providers and we providing financial services all over Australia.
We also provide Xero Training & ongoing support to all our clients as and when needed. Get in touch with us today to take the first step on your stairs of success.
We completely understand how busy you are, and with our expertise we can take care of your accounting needs quickly and professionally.
AMA Accountants
Company Statistics
20,000 +
Returns Annually
20 +
Tax Consultants
20 M
In Claimed Deductions
25 +
Years Experience
Get In Touch
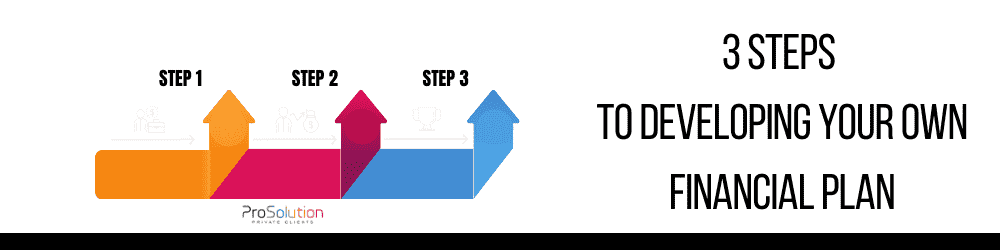
Our Process


Shreya Kohli
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Nayan Barik
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Cesario Jr. Samarita
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Ashish Saxena
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Amarjit
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Harsh Khandewal
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Ripu Daman
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Joey
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Anuj Malik
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Amandeep Singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Shalin Shah
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jatinder singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Virk Chandan
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Prashant Sumeet
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

harjot kaur
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Lovejot Khosa
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Girish Bakhshi
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Lovepreet Bawa

Damanpreet Singh

Kuljit Kaur

Max Fenner

Ei Sandar

Ravinder S

dilpreet singh

Chander Sharma

Vajid Mukhi

Richa Sharma

singhsammy8 singh

Ranard Mak

toni brennan

Vatan Kotlia

Jaspreet Singh

harmeet dhillon

Laxman Regmi

Sajy Augusty

kritika kaushal

nema kwa

NEHA GUJRAL

Dav D

Maxime Ribault

Jacob Leonardo

Virat Singh

Ashmit Kumar

Mandeep Thakur

Nikki U

Dhruvin Mehta

Happiness Bishnoi

Haryanvi Tadkaa

Mandeep Singh
Abhinav Khandelwal
Vasudev Narasimhaswamy
Venkatesh Velisala
Skilled hand service
Prince Prince
Rhiannon Walker
Manveer Kang
Dishant Rupani
Gurjas Singh
KANWARJEET SINGH
Karina Fabijan
Ream Clarke
Mounira Abdallah
Bhagya Parmar
Abhinav Khandelwal
Shivam Vij
Maninder kaur
Dhruv Patel
krishnadas s
Dip K
Dilbag Singh
avinderjeet billing
Saab Singh
Vasudev Narasimhaswamy
Venkatesh Velisala
Bardot Rustanto25
Naveed Kashif
Aman Saini
Ellie Carr
Amritpal Singh
Ranjeet kaur
Gurpinder Singh
Oksana Kompanets
AMARJEET GABA
Dai Nguyen
Mohinder Singh
Anil Kumar
Vishal Jangra
Virender Saini
Kajal ani

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

KOMAL DEVI
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Sahil chaudhary
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Neha Chander
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Gurpreet Sangoo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Harpreet Kaur
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

John Nghiem
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Puneet Kumar
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

aksham. Chaudhary
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Navneet Singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Shreya Kohli
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Nayan Barik
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Cesario Jr. Samarita
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Ashish Saxena
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Amarjit
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Harsh Khandewal
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Ripu Daman
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Joey
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Anuj Malik
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Amandeep Singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Shalin Shah
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jatinder singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Virk Chandan
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Prashant Sumeet
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

harjot kaur
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Lovejot Khosa
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Girish Bakhshi
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Lovepreet Bawa

Damanpreet Singh

Kuljit Kaur

Max Fenner

Ei Sandar

Ravinder S

dilpreet singh

Chander Sharma

Vajid Mukhi

Richa Sharma

singhsammy8 singh

Ranard Mak

toni brennan

Vatan Kotlia

Jaspreet Singh

harmeet dhillon

Laxman Regmi

Sajy Augusty

kritika kaushal

nema kwa

NEHA GUJRAL

Dav D

Maxime Ribault

Jacob Leonardo

Virat Singh

Ashmit Kumar

Mandeep Thakur

Nikki U

Dhruvin Mehta

Happiness Bishnoi

Haryanvi Tadkaa

Mandeep Singh
Abhinav Khandelwal
Vasudev Narasimhaswamy
Venkatesh Velisala
Skilled hand service
Prince Prince
Rhiannon Walker
Manveer Kang
Dishant Rupani
Gurjas Singh
KANWARJEET SINGH
Karina Fabijan
Ream Clarke
Mounira Abdallah
Bhagya Parmar
Abhinav Khandelwal
Shivam Vij
Maninder kaur
Dhruv Patel
krishnadas s
Dip K
Dilbag Singh
avinderjeet billing
Saab Singh
Vasudev Narasimhaswamy
Venkatesh Velisala
Bardot Rustanto25
Naveed Kashif
Aman Saini
Ellie Carr
Amritpal Singh
Ranjeet kaur
Gurpinder Singh
Oksana Kompanets
AMARJEET GABA
Dai Nguyen
Mohinder Singh
Anil Kumar
Vishal Jangra
Virender Saini
Kajal ani

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

KOMAL DEVI
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Sahil chaudhary
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Neha Chander
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Gurpreet Sangoo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Harpreet Kaur
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

John Nghiem
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Puneet Kumar
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

aksham. Chaudhary
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Navneet Singh
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Jacob Leonardo
Senior Manager of Excel Solution

Shreya Kohli
Senior Manager of Excel Solution